Decoding the Brain: NeuroImageGen AI Model Decode the Brain Signals to Reconstruct Visual Memories
Exploring the Intersection of Brain Activity and Visual Perception
The human brain, a marvel of nature, holds the key to life’s mysteries. Understanding its intricacies, from thought processes to sensory perception, is crucial. It’s all about comprehending how the brain functions.
One exciting avenue of research involves deciphering how the brain reacts to visual stimuli. This knowledge could pave the way for advanced computational cognitive systems. Thanks to tools like functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalograph (EEG), we can now record brain responses triggered by what we see. This has sparked immense interest in decoding and reconstructing the actual content that stimulates the human brain.

A New Approach to Visual Perception
One common method for studying human visual perception is reconstructing the images or videos subjects viewed during experiments. This involves computational techniques, especially deep neural networks, and relies heavily on fMRI data. However, collecting fMRI data is expensive and uncomfortable. Few willingly participate in experiments involving MRI devices.
Enter EEG, the Game Changer
EEG offers a more efficient way to record and analyze brain signals as subjects view stimuli. But it comes with its own set of challenges. EEG signals are time-series data, unlike static images. This makes matching stimuli to corresponding brain signals a complex task. Additionally, issues like electrode misplacement and body movement can introduce substantial noise into the data. Simply mapping EEG inputs to pixels for image reconstruction leads to low-quality results.
The Promise of Diffusion Models
In the realm of generative modeling, diffusion models have emerged as state-of-the-art tools. They’ve found success in tasks like image synthesis and video generation. By operating in the latent space of powerful pre-trained autoencoders, researchers have overcome the limitations of pixel space evaluation. This enables quicker inference and reduces training costs.

Meet NeuroImageGen: Bridging the Gap
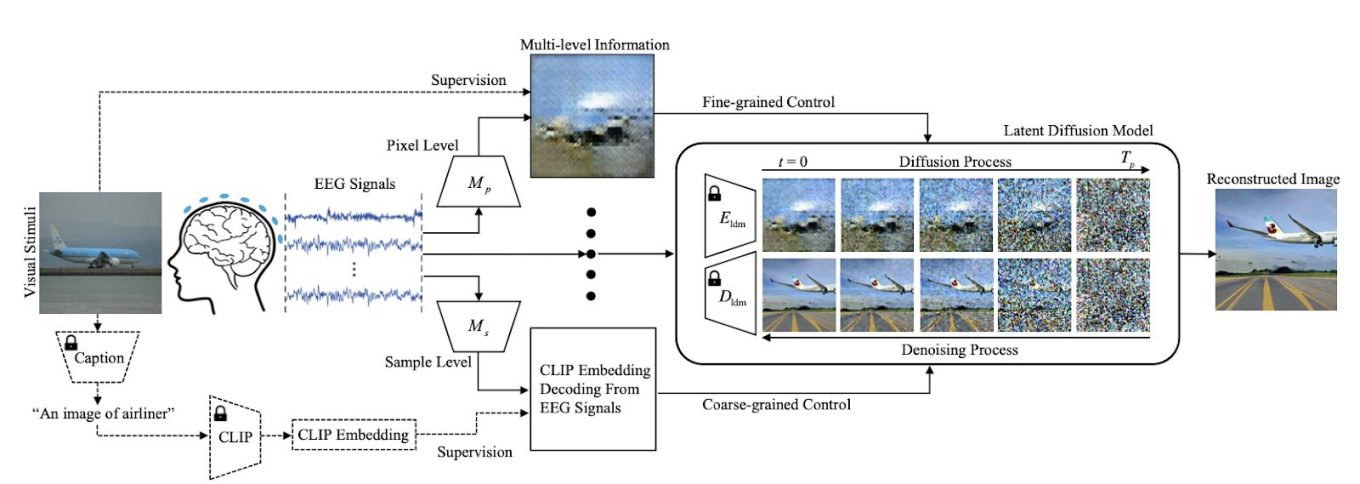
NeuroImageGen is a cutting-edge pipeline for neural image generation using EEG signals. It tackles the challenges associated with EEG-based image reconstruction head-on. How? By incorporating a multi-level semantics extraction module. This module decodes various levels of semantic information from EEG signals, ranging from sample-level semantics to pixel-level details like saliency maps. These multi-level outputs then feed into pre-trained diffusion models, effectively governing the generation process at multiple semantic levels.
Navigating the Complexity of EEG Data
EEG signals, being complex time-series data, are prone to noise. NeuroImageGen tackles this issue by extracting multi-level semantics. This includes both pixel-level and sample-level information. Pixel-level semantics capture fine-grained details like color, position, and shape through saliency maps. Sample-level semantics provide a broader understanding, such as recognizing image categories or text captions. This multi-level approach equips NeuroImageGen to handle noisy EEG data effectively, resulting in high-quality visual stimulus reconstruction.
The Magic of Integration
NeuroImageGen seamlessly integrates these multi-level semantics into a latent diffusion model for image reconstruction. Pixel-level semantics, represented as saliency maps derived from EEG features, form the basis for the initial image. Sample-level semantics, derived from CLIP model embeddings of image captions, guide the denoising process within the diffusion model. This integration allows for flexible control of semantic information at various levels during reconstruction, ultimately producing high-quality images.
Promising Results
The results of this approach are highly promising, surpassing traditional image reconstruction methods for EEG data. NEUROIMAGEN significantly enhances the structural similarity and semantic accuracy of reconstructed images, shedding light on how visual stimuli impact the human brain.
Also See:
iPhone 15 release date, specs, and complete launch details
Samsung Galaxy A25 5G Specs Revealed in Recent Leaks
Apple Reveals iPhone 15 Pro and iPhone 15 Pro Max with Specs
Motorola Introduces Moto G84, G54 Power, and G54 to European Market
Stability AI Introduces Stable Doodle: A Revolutionary Sketch-to-Image Tool
iTiny 12 Pro Max Specs, Camera and Features – Compact Smartphone
Nokia N820 Specs – Next level Smartphone



Great information in your post. Good Work. Keep it up.
impressive Technology. Great development in AI.