RAID for hard drives: what it is, what it is for and all the benefits it offers to your computer

When you are looking to improve the performance and security of your computer, you may come across the RAID technology. You may have seen this specification in the features of a high-end PC, a server, or even on your computer, and wondered What it means and how it can benefit you.
Did you know that hard drives are not only used to store your files, but they can also be combined to create a more powerful and secure storage unit?
This is achieved with a RAID configuration where you can Connect multiple hard drives to your computer’s motherboard and make them work as one, thus increasing its capacity, speed and reliability. It’s like having a super hard drive made up of several smaller disks.
What is RAID and what benefits does it bring to your computer?
RAID, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is a technology that combines multiple storage drives into a single logical drive. This is achieved by grouping two or more hard drives to improve system performance, capacity, or reliability.
By combining multiple hard drives into one, RAID can significantly increase the speed of reading and writing data. This is especially useful in applications that require quick access to large amounts of information, such as video editing, graphic design, or database servers.
Likewise, security increases, since, depending on the type of configuration used, data security can also be improved. By automatically mirroring data across multiple hard drives, RAID can provide protection against data loss in the event of a hard drive failure.
By distributing the workload across multiple disks, the Redundant Array of Independent Disks It can also improve system reliability. In the event of a disk failure, the system can continue to function without problems, since data is duplicated on other disks.
RAID Types
Intel
There are up to 15 different types of RAIDeach with its own advantages and disadvantages, but the most common types are RAID 0, RAID 1 and RAID 5.
The type of RAID you need will depend on your specific needs. If you need maximum speed, RAID 0 is the best option. If you need redundancy to protect your data, RAID 1 or RAID 5 are the alternatives.
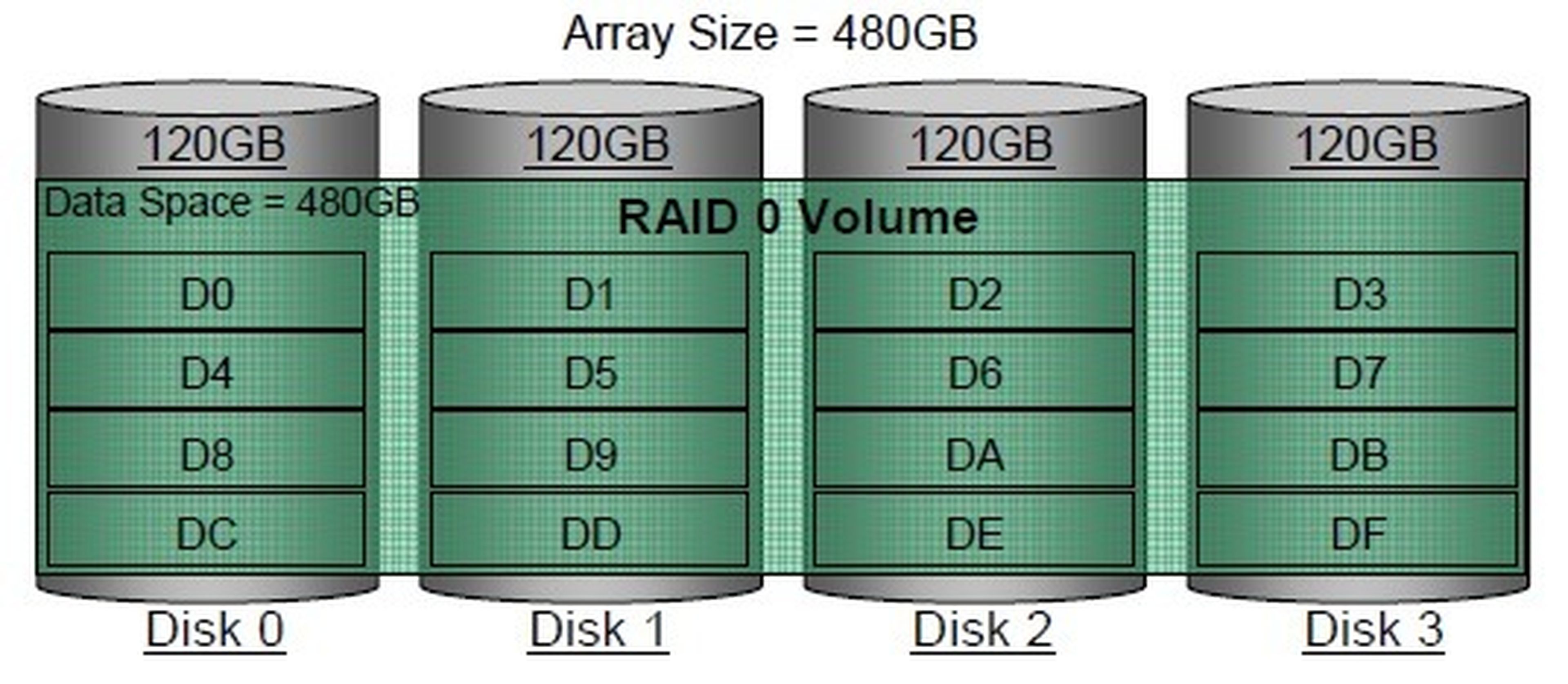
RAID 0: Also know as stripe set either striping, divides the data into blocks and distributes them between two or more hard drives. This significantly improves performance as data can be written to and read simultaneously from multiple disks.
RAID 1: Duplicate data across two or more hard drives. Each data is written to different disks, providing an exact copy of the data in the event of a disk failure. It offers high reliability and fault tolerance, but does not improve performance because data is written twice.
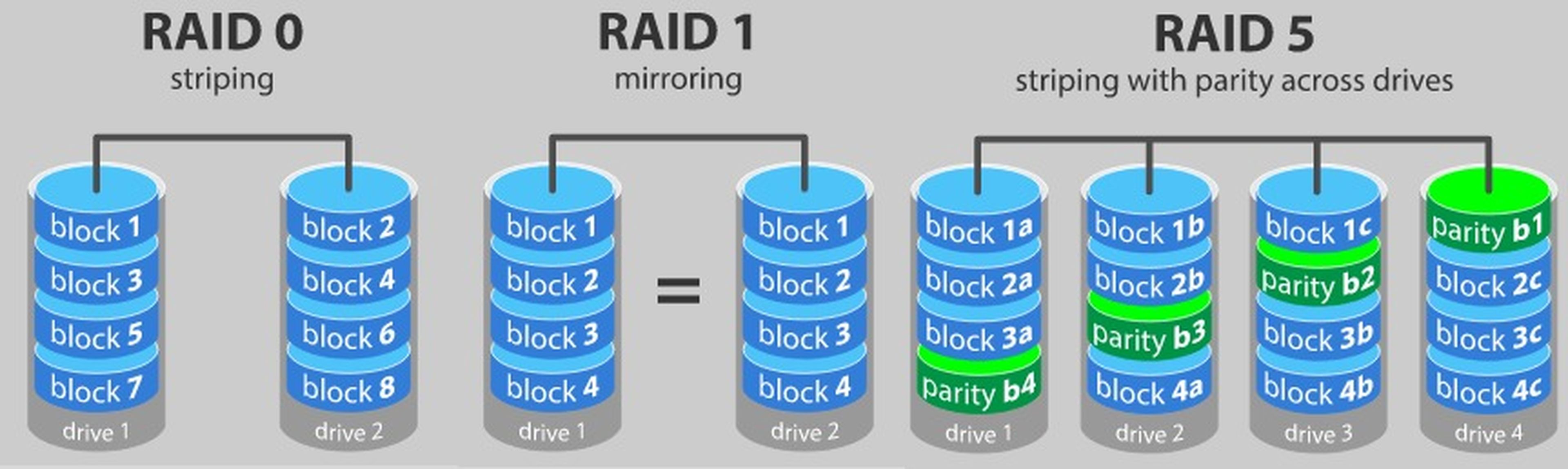
RAID 5: Use striping with distributed parity between three or more hard drives. Parity is distributed across the disks, providing efficient data redundancy and a good balance between performance and security. It can tolerate the loss of one disk without losing data, but requires at least three disks to function.
RAID 6: It is similar to RAID 5 in that it uses striping with double parity distributed among four or more hard drives. This provides greater fault tolerance in that it can withstand the loss of up to two disks without losing data. It offers additional security, but may have slightly lower performance due to the additional overhead.
RAID 10 or RAID 1+0: Combines features of RAID 1 and RAID 0, where data is mirrored across multiple disks, then spread across striping. In the end, it provides both high reliability and high performance, but requires at least four drives to operate.
These are just some examples of the most common types of RAID configurations. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the right RAID type will depend on your specific performance, capacity, and security needs.
It should be noted that Any computer supports RAID configurations, although not all are compatible. It all depends on the processor, which is the set of chips that control the motherboard.
Each manufacturer and each chipset model has its own RAID options, so if you want to use this technology, you have to look carefully at the specifications of your motherboard in your computer.
For example, a high end motherboard may have a chipset that supports RAID 0, 1, 5 and 10, which are commonly Intel models, while a low end motherboard only RAID 0 and 1 support, which is found on AMD boards and chips.
These are the only RAID configurations that are supported because they are the ones that offer benefits to the average user. However, the other configurations are either complicated to implement or very expensive, and are reserved only for professional environments.